Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Polish forests
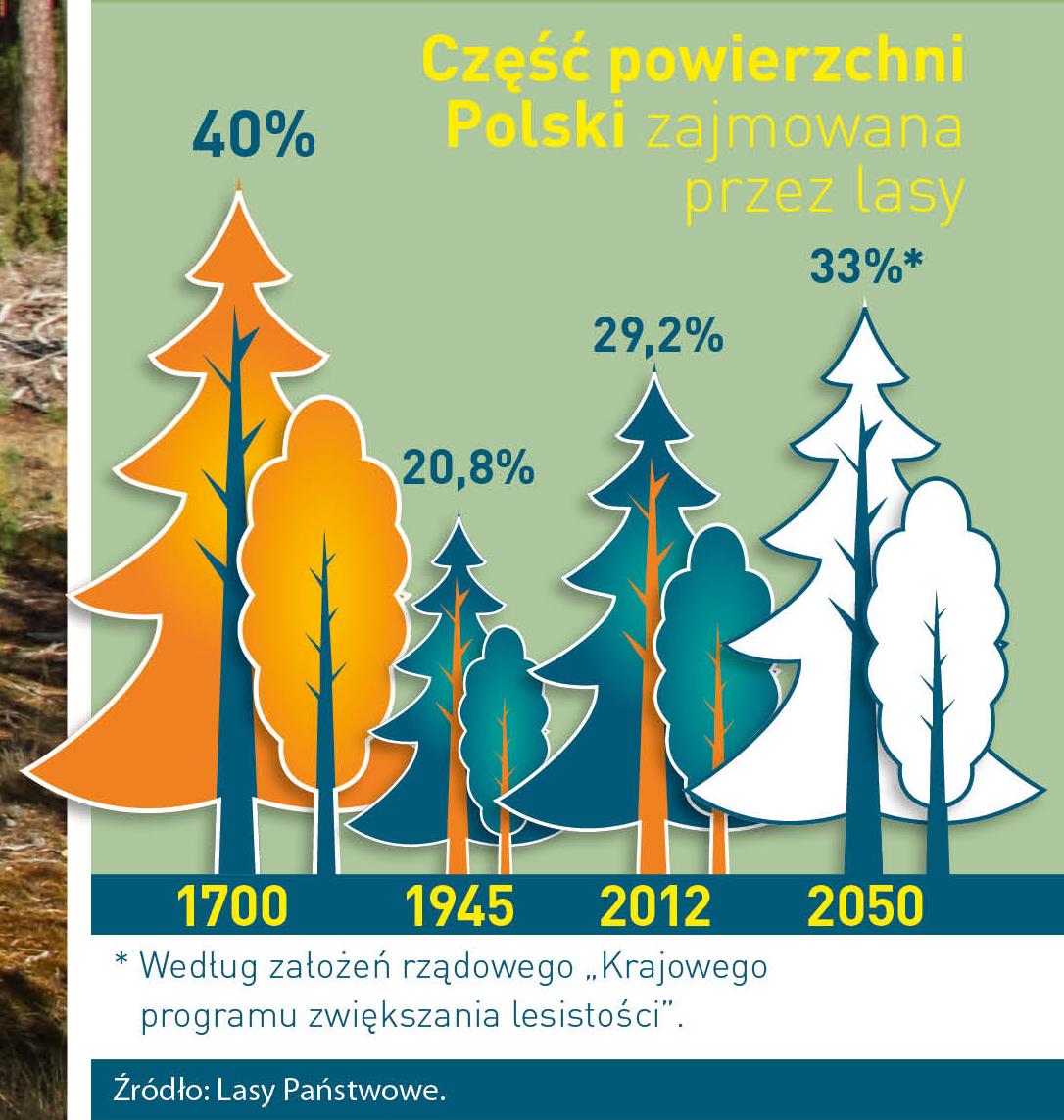
Poland is in the European lead, while concerning the area of all forests. They cover about 29,2 % of the country territory, and grow within the area of 9,1 million hectares. The overwhelming majority of the forests is state owned, of which almost 7,6 million hectares are managed by the State Forests National Forest Holding..
The number of Polish forest is still growing. The forestation rate of the country has increased from 21 % in 1945 to 29,2 % at the moment. Between 1995 and 2008, the forest area increased by 310 thousand ha. The basis for afforestation works is the "National Programme for Increasing the Forest Cover" (KPZL), assuming an increase of the forestation rate up to 30 % by 2020 and up to 33 % by 2050. Polish forests abound in flora, fauna and fungi. 65 % of the total number of animal species live there.
The forests grow in our country on poor soils, mainly because of the development of the agriculture in previous years. It influences the distribution of the types of the forest sites in Poland. Over 55 % of the forest areas is covered with coniferous forests. In other areas, there are forest sites, mainly the mixed ones. Their small part constitute alder and riparian forests – not more than 3 %.
In the years 1945 – 2011 the area of natural deciduous tree stands within the area of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %.
Within the lowlands and uplands the most often occurring tee species is pine. It covers 64,3 % of the forest area of the State Forests National Forest Holding and 57,7 % of private and commune forests. In the mountains the predominant species is European spruce ( in the west) and European spruce with beech (in the east). Domination of pine is the result of carrying on sustainable forest management in the past. Once, the monocultures (crops or cultivations of one species) were the answer to the great demand of industry for wood. Such forests appeared to be quite fragile to climatic factors. They also were often the prey of pests' expansion.
In Polish forests, the share of other tree species, especially deciduous trees have been systematically increasing. The foresters have stepped aside from monocultures – that is why, they try to fit specific species of the forest stand to the natural stand, that would be proper for the given area. Thanks to that, in the years 1945 – 2011, the area of the deciduous tree stands within the lands of the State Forests National Forest Holding increased from 13 to 28,2 %. There occur more and more frequently the following tree species: oaks, ashes, maples, sycamore maples, elms, but also birches, beeches, alders, poplars, hornbeams, aspens, tilias and willows.
Our forests are the most often represented by the forest stands aged 40 to 80 years. The average age of the forest equals 60 years. More and more trees are of big size at the age over 80 years. Since the end of the Second World War, the forests' area has increased up to almost 1,85 million hectares.
Raport o stanie lasów w Polsce 2012
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
 Asset Publisher
Asset Publisher
Rezerwaty
Rezerwaty
 6 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
6 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
 1 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
1 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
 2 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
2 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
 3 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
3 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
 7 Rezrwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
7 Rezrwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
 8 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
8 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
 9 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
9 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
 13 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
13 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
 5 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
5 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
 11 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
11 Rezerwat Węże-K.Bednarek.JPG
Rezerwaty to wydzielone obszary o szczególnych wartościach przyrodniczych, zachowane w stanie naturalnym lub mało zmienionym. Ogranicza się tam gospodarkę leśną. Spośród 1441 rezerwatów, które mamy obecnie w Polsce, 671 to rezerwaty leśne o łącznej powierzchni ponad 61 tys. ha. Rezerwaty stanowią 1,6 proc. powierzchni lasów zarządzanych przez LP.
Rezerwaty przyrody i inne formy ochrony przyrody na terenie nadleśnictwa
Na terenie Nadleśnictwa Wieluń występują 4 rezerwaty przyrody:
- Rezerwat "Lasek Kurowski"
- Rezerwat "Mokry Las"
- Rezerwat "Dąbrowa Niżankowicka"
- Rezerwat "Węże"
Łączna powierzchnia rezerwatów wynosi około 160 ha.
Na terenie rezerwatów ochroną objęte są gatunki drzew rodzimego pochodzenia, takie jak: sosna, jodła, dąb, olsza i brzoza tworzące drzewostany od III do VIII klasy wieku na siedliskach wilgotnych. Drzewostany te są dobrej jakości technicznej i hodowlanej.
"Bo na tym świecie, wszystko się miecie, w dolinę upadnie góra, tylko trwa stale to boskie dziecię, wieczna, niezmienna: Natura!" K. Ujejski
Rezerwat "Mokry Las" to obiekt chroniący fragmenty lasów grądowych z udziałem jodły, grądów niskich i lasów łęgowych, stanowiących relikty zbiorowisk leśnych pokrywających niegdyś cały obszar uroczyska, w którym rezerwat jest położony. Teren rezerwatu stanowi więc lokalną ostoję gatunków flory i fauny, które związane są z siedliskami niskich torfowisk i łęgów oraz wilgotnych grądów.
Rezerwat "Lasek Kurowski" to obiekt chroniący lasy z udziałem jodły przy granicy zasięgu występowania tego gatunku, to dobrze zachowane fragmenty lasów grądowych oraz olsów. Największy udział w drzewostanie stanowi olsza z domieszką świerka i dęba.
Lasek Kurowski - fot. M. Mazur
Rezerwat "Dąbrowa Niżankowicka" - gatunkiem dominującym jest dąb bezszypułkowy z domieszką sosny i brzozy brodawkowatej. Drzewostany dębowe są pozostałością lasów niegdyś rozpowszechnionych w tym regionie i stanowią rzadkie już dzisiaj skupiska lasu liściastego.
Dąbrowa Niżankowicka - fot. P.Wysocki
Rezerwat "Węże" to jedyny na terenie Nadleśnictwa rezerwat geologiczny, stworzony w celu ochrony wzgórz wapiennych, z systemem krasowym i osadów krasowych zawierających szczątki zwierząt kopalnych. Ponadto celem rezerwatu jest także ochrona charakterystycznej nawapiennej roślinności naskalnej oraz muraw kserotermicznych. Rezerwat ten znajduje się w północnej części geologicznej jednostki określanej jako Jura Polska.
Od 1 stycznia 2004 roku Rezerwat HOŁDA został przekazany do Nadleśnictwa Złoczew w wyniku zmian terytorialnych.


 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański
 fot. Paweł Fabijański
fot. Paweł Fabijański